RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit data between an RFID tag and the reader. The frequency of the tag determines its read distance and affects its functionality.
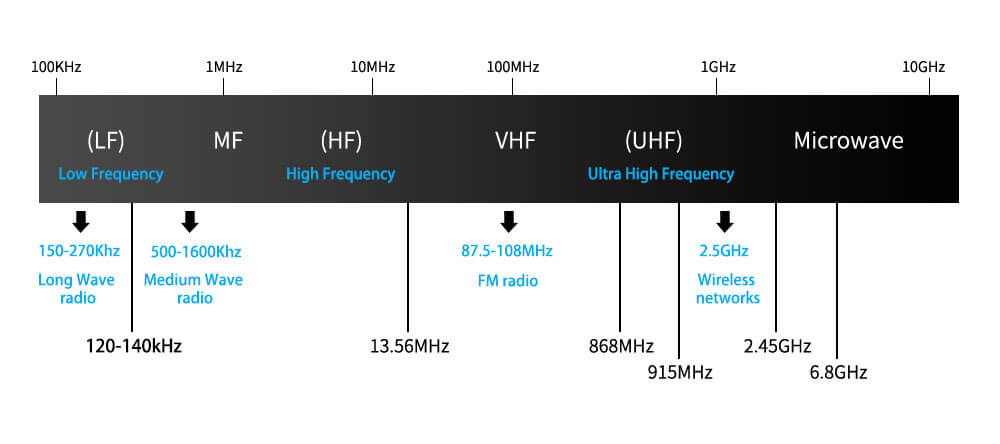
The three primary frequencies used with RFID devices include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF).
But what’s the difference between these frequencies?
Well, each of the three frequencies behaves differently when used with RFID devices. As such, you should choose a tag with an ideal frequency to undertake your desired functions.
This article enumerates the features, advantages, and disadvantages of each of the frequencies for your consideration.
What is Frequency?
Frequency refers to the number of waves passing through a fixed object in a given time. For example, if a wave takes 0.5 seconds to pass through an object, then the frequency will be two waves per second.
The higher the frequency, the higher the number of waves that pass through that particular object per given time (usually per second).
Frequency is measured using a unit called Hertz (Hz), where Hz represents one wave. Since many waves will pass through objects per second, the unit is further classified as follows:
- Kilohertz (kHz). This refers to one thousand hertz
- Megahertz (MHz). This unit represents one million hertz
- Gigahertz (GHz). The unit refers to one billion hertz
- Terahertz (THz). Refers to one trillion hertz
An ordinary radio spectrum ranges from 3 kilohertz to up to 3000 gigahertz.The frequency of any given RFID device will affect its functionality.
For example;
A low-frequency tag will only have a read range of approximately 10 cm, while an ultra-high frequency tag will have a read range of up to 100 meters.
What is Low Frequency? Definition and Brief Description
Low frequency means that the number of waves passing through an object is fewer than the high frequency.
Its frequency ranges from 125 kHz to 134 kHz.
This range means that approximately 125,000 to 134,000 waves will pass through the object every second when utilizing an LF device.
Features of Low Frequency
- Frequency ranges from 30 kHz to 300 kHz. However, the best operation frequency is 125 kHz
- Have a short read range of up to 10 cm
- Low chances of radio wave interference
- Slower read speed
- Longer wavelengths
Advantages of Low Frequency
- Have longer wavelengths, which makes it easier for them to penetrate metallic objects. This feature makes the tags work best with metallic objects.
- It has lower chances of radio wave interference. This feature makes it easy for you to use the LF tags in a highly electromagnetic environment.
- Works optimally on liquid surfaces
Disadvantages of Low Frequency
- Slow data transfer rates. You cannot use these tags if you want a system that can read multiple tags simultaneously.
- Short read range. For your reader to capture data, the LF tag must be at most 10 centimeters away. This feature is highly limiting since you cannot apply the technology to track far-apart assets.
High Frequency: Definition
The high-frequency band covers all frequencies between 3 MHz and 30 MHz. However, RFID HF systems operate at a standard frequency of 13.56 MHZ.
The frequency has a relatively more comprehensive read range compared to the LF. As such, HF tags are ideal for tracking items up to 1 meter away from the reader.
What are the Features of High Frequency?
- The band covers frequencies of 3-30 MHz
- Have a read range of between 10 cm and 1 meter
- They are moderately sensitive to interferences by other radio waves
- Can be used in ticketing and contactless payment systems
Advantages of High Frequency
- They can operate in a relatively moist environment.
- Relatively fast data transfer rates compared to the LF.
- Regulated by several HF standards, including ISO 15693 for object tracking and ISO/IEC 14443A & ISO/IEC 14443 standards for MIFARE use.
- A wider read range of up to 1 meter.
- More affordable than the LF tags.
Shortcomings of High Frequency
- Not best when you need a reader to read many tags simultaneously, but better than LF
- Have a moderate chance for radio-wave interference
What is Ultra-High Frequency?
Ultra-High frequency band covers all frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. It offers a read range of up to 12 meters. Most of the UHF systems operate within the 900 MHz and 915 MHz range. This frequency is usually used in making toll payments and managing parking systems.
Features of Ultra-High Frequency
- Has a read range of up to 40 feet/ 12 meters
- Cheapest tag in the market
- Complies with UHF Gen2 standard (ISO 18000-63)
- Fastest growing RFID segment
Advantages of UHF
- Cheaper than both HF and LF
- The tags have a wide read range of up to 12 meters
- Has the quickest data transfer rate when compared to LF and HF
Disadvantages of UHF
- The most sensitive frequency. It is prone to radio waves interference
- Does not work on metallic and liquid surfaces
What Is the Difference Between Low Frequency, High Frequency, and Ultra High Frequency?
All these frequencies use radio waves to transmit data. However, the number of waves that pass through objects differs significantly.
These differences affect their features and functionality. For example, low-frequency tags offer fewer but long wavelengths that are ideal for use with metallic and liquid objects. The long wavelength makes it easy to penetrate metallic objects. On the downside, these tags will only offer a limited read range of up to 10 cm.
These features make LF tags the best for use when:
- Tracking fruits, vegetables, beverages, and other high-water content substances
- Animal tagging
- Access control (can be used with access cards due to their limited read range)
The high-frequency tags have a relatively wider read range of up to one meter. As such, you should choose these tags when you need to track objects without necessarily getting too close to them. For example, if you want to use a portable reader to locate items in your store, then the HF tags would be ideal.
Also, HF tags have a limited ability to penetrate metallic objects. It also works well with substances with medium to high water content. Some of these tags’ key applications include tracking patients’ progress in hospitals, tracking library books, and transportation.
Related articles:
- Unique Features and Benefits of Custom RFID Tags
- What are RFID Standards? An All-Inclusive Guide
- A Guide to Buying RFID tags and Equipment.
- What are RFID wristbands- How does it work?
- 6 Crucial Factors that Affect RFID Read Range – A Detailed Guide
- A Guide to RFID Tags Types And What are they Difference